Outward Indications Of Bursitis Of The Feet
In the ankle, 2 bursae are found at the level of insertion of the Achilles tendon. The superficial one is located between the skin and the tendon, and the deep one is located between the calcaneus and the tendon. The latter is the one more commonly affected by bursitis.
Causes
A rapid increase in physical activity levels or thinning of the heel?s protective fat pad are factors that may contribute to infracalcaneal bursitis. Other possible causes of infracalcaneal bursitis include blunt force trauma, acute or chronic infection, and arthritic conditions. The following factors may increase your risk of experiencing bursitis, including infracalcaneal bursitis. Participating in contact sports. Having a previous history of bursitis in any joint. Poor conditioning. Exposure to cold weather. Heel striking when running, especially in conventional running shoes with heel elevation.
Symptoms
When the bursa becomes inflamed after an injury, symptoms usually develop suddenly. When the bursa develops without an injury, symptoms may develop gradually. With both posterior and anterior Achilles tendon bursitis, symptoms usually include swelling and warmth at the back of the heel. A minimally red, swollen, tender spot develops on the back of the heel. When the inflamed bursa enlarges, it appears as a red lump under the skin of the heel and causes pain at and above the heel. If posterior Achilles tendon bursitis becomes chronic, the swelling may become hard, fluid-filled, and red or flesh-colored.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist may be all that is necessary to diagnose a retrocalcaneal bursitis. Diagnosis may be confirmed with an ultrasound investigation, MRI or CT scan.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you follow these steps, most attacks of bursitis should subside in four or five days and all symptoms should be gone within two weeks. Rest the body part that hurts. If you suspect that one activity has caused the pain, stop it until the pain is entirely gone. A sling, splint, or padding may be needed to protect the area from possible bumps or irritation. Try over-the-counter pain relievers. Nonprescription NSAIDs (aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen) will help reduce pain and swelling, though they won?t accelerate healing. Acetaminophen will help with pain but it doesn?t reduce inflammation. Ice it, then heat it. Apply ice packs during the first two days to bring down swelling. Then use heat-warm baths or a heating pad (on a medium or low setting)-to ease pain and stimulate blood flow. Don?t push it. Resume exercising only after you feel better. Start with gentle activity. Skip the liniments. Liniments and balms are no help for bursitis. Liniments don?t penetrate deeply enough to treat bursitis, they mainly warm the skin and make it tingle, thus distracting attention from the pain beneath. Massage is likely to make matters worse. Undergo physical therapy. Physical therapy strengthens joint muscles that have been affected by bursitis and may help prevent the bursitis from getting worse.
Surgical Treatment
Only if non-surgical attempts at treatment fail, will it make sense to consider surgery. Surgery for retrocalcanel bursitis can include many different procedures. Some of these include removal of the bursa, removing any excess bone at the back of the heel (calcaneal exostectomy), and occasionally detachment and re-attachment of the Achilles tendon. If the foot structure and shape of the heel bone is a primary cause of the bursitis, surgery to re-align the heel bone (calcaneal osteotomy) may be considered. Regardless of which exact surgery is planned, the goal is always to decrease pain and correct the deformity. The idea is to get you back to the activities that you really enjoy. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the exact surgical procedure that is most likely to correct the problem in your case. But if you have to have surgery, you can work together to develop a plan that will help assure success.
How To Treat Hammertoes
 Overview
Overview
A hammertoes is a deformity of the middle joint of a toe, producing a clenched, clawlike appearance in the affected digit. The tendons in the toe become abnormally contracted, causing the toe to bend downward, which, in turn, forces the joint to protrude upward. A mallet toe is a deformity in which the end joint of a toe becomes bent downward, so that the toe curls underneath itself. In either case the affected joints are stiff, and often the toe cannot be straightened out. Constant rubbing against shoes may furthermore cause a painful corn (a round patch of rough, thickened, calloused skin) to develop over the joint or at the tip of the affected toe. Hammer and mallet toes may occur in any toe, although the second toe is the most common site. These deformities are often painful and limit the toe?s range of motion-sometimes requiring surgery.
Causes
The muscles of each toe work in pairs. When the toe muscles get out of balance, a hammer toe can form. Muscle imbalance puts a lot of pressure on the toe's tendons and joints. This pressure forces the toe into a hammerhead shape. How do the toe muscles get out of balance? There are three main reasons. Your genes, you may have inherited a tendency to develop hammer toes because your foot is slightly unstable - such as a flat foot. But high-arched feet can also get hammer toes. Arthritis. Injury to the toe: ill-fitting shoes are the main culprits of this cause. If shoes are too tight, too short, or too pointy, they push the toes out of balance. Pointy, high-heeled shoes put particularly severe pressure on the toes.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A soft corn, or heloma molle, may exist in the web space between toes. This is more commonly caused by an exostosis, which is basically an extra growth of bone possibly due to your foot structure. As this outgrowth of excessive bone rubs against other toes, there is friction between the toes and a corn forms for your protection.
Diagnosis
Although hammertoes are readily apparent, to arrive at a diagnosis the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain a thorough history of your symptoms and examine your foot. During the physical examination, the doctor may attempt to reproduce your symptoms by manipulating your foot and will study the contractures of the toes. In addition, the foot and ankle surgeon may take x-rays to determine the degree of the deformities and assess any changes that may have occurred.
Non Surgical Treatment
Prescription strength medicines to decrease pain and inflammation. Physical Therapy. To strengthen poorly functioning muscles and stretch tight muscles that may be exacerbating the toes. Special ultrasound techniques may reduce inflammation. Custom Foot Orthotics. An orthotic with an exact mold of your foot to better align and support the foot to ease current discomfort and prevent future progression. Toe Splints or Pads. Specific pads may prevent pressure and physical irritation in shoes. Toe splints and toe spacers physically realign the toes and can lessen pain and halt or stall hammer toe progression. Cortisone injections are strong anti-inflammatory agents to decrease pain, and swelling directly at the toe region. Injections only treat the symptoms, and in some cases used in caution (and sparingly) they can weaken supporting ligaments of the toe(s).
Surgical Treatment
If your toe is not bendable, your doctor may recommend surgery. The type of surgery that will be performed will depend on the severity of the condition. You should expect blood and urine studies before the procedure, as well as x-rays of your feet. Your doctor will inject either hammertoe a local or regional anesthetic. If your toe has some flexibility, the doctor may be able to straighten it by simply making an incision in the toe to release or lengthen the tendon. If the toe is not flexible, your doctor will probably make the same incision to release the tendon, but he or she may also remove some pieces of the bone so that the bone can be straightened. A k-wire is placed in the toe to help hold it straight while it is healing. This is taken out after about four weeks.
 Prevention
Prevention
It?s important to understand that preventing hammertoe can sometimes be difficult, since most symptoms do not appear until the condition is well developed. Nonetheless, here are some tips to help you prevent hammertoe. Do not wear shoes that are too narrow or short. Check your children?s shoe size often to ensure that their shoes still fit correctly. Wear comfortable shoes that fit you properly. Remember that your feet widen and lengthen with age.
What Does Overpronation Mean
Feet are supposed to roll inward as a part of every step you take. This helps them to mold to the various terrain that they step on (sand, rocks, various obstacles) without injury. This is called pronation. But, when your feet roll inward excessively, problems often arise. Excessive inward rolling of the feet and ankles is called over-pronation. Sometimes, people who over-pronate are told they have ?flat feet?. The term ?flat feet? can be misleading. When standing, body weight causes the arch of most feet to flatten out somewhat. This does not mean they become flat like pancakes (though some feet do). Instead, the arch shape gets longer and flatter and the arch height gets lower.
Causes
There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.
Symptoms
Symptoms can manifest in many different ways. Here is a list of some of the common conditions associated with over-pronation in children. Achilles Pain. Ankle pain. Arch Pain. Low back pain. Heel Pain. Knee Pain (Runner's knee and Chondromalecia of the patella) Osgood Schlatter Disease (pain below the knee) Shin Splints (pain in the front of the lower leg) Over-pronation does not necessarily mean your child has "flat feet." Even though children's arches may be relatively high when they lie down or sit, over-pronation may not be seen until your child is standing. A certain amount of pronation is normal. During normal walking or running ("gait cycle"), the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward to absorb shock and adapt to the surface. This gait cycle is even more important if the running surface is uneven.
Diagnosis
You can test for pronation by looking at the leg and foot from the back. Normally you can see the Achilles Tendon run straight down the leg into the heel. If the foot is pronated, the tendon will run straight down the leg, but when it lies on the heel it will twist outward. This makes the inner ankle bone much more prominent than the outer ankle bone.

Non Surgical Treatment
Anti-Pronation Insoles provide a unique foot support system that aligns the lower body. The major cause of foot and leg pain is over pronation (rolling over of the feet) which causes excessive pressure on the muscles, ligaments and bones of the lower body. Running insoles treat the underlying cause of over pronation and prevent future occurrences of the associated foot or leg condition. A project conducted at the NIKE Sport Research Laboratory studied the effects of orthotics on rear foot movement in running. Nine well-trained runners who wore orthotics were chosen as subjects. The results of the study indicated that orthotics reduced rear foot movement by roughly one degree or approximately nine percent of the amount found in runners not using orthotics. The average reduction of the maximum velocity of pronation was fifteen percent. Thus this study indicates that orthotics and insoles control over pronation which will treat and prevent many sporting injuries.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. The ankle and hindfoot bones/midfoot bones around the joint are fused, locking the bones in place and preventing all joint motion. This may also be done in combination with fusion at other joints. This is a very aggressive option usually reserved for extreme cases where no joint flexibility is present and/or the patient has severe arthritic changes in the joint.
How You Can Diagnose Severs Disease?
If your child is limping, having difficulty walking, complaining of pain in their heels upon waking up in the morning or experiencing swelling or redness in the heel, it's extremely important that you pay attention to their symptoms and seek expert medical help as soon as possible. Heel pain in adolescents is frequently a sign of a condition known as Sever's Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis), and while this is not a life-threatening condition, it can lead to debilitating symptoms for your child which should be remedied as quickly as possible. This article provides an easy-to-read introduction to the causes of and treatment options for Sever's Disease. By educating yourself on this important topic, you will be ready to seek the right help for your child so that he or she can regain their health and be free of pain again.
Causes
Heel pain is very common in children because of the very nature of their growing feet and legs. In children, the heel bone (the calcaneus) is not fully developed until the age of 14 or older. Until then, new bone is forming at the growth plate of the foot (the apophysis, located at the back of the heel), an area which is softer than others due to its role in accommodating the growth. Repetitive stress on the growth plate due to walking, running and sports causes inflammation in the heel area. Because the heel's growth plate is sensitive, repeated running and pounding on hard surfaces can result in pediatric heel pain. Children and adolescents involved in football, soccer, running or basketball are especially vulnerable. Over-pronation (fallen arches and rolling inwards of the feet) will increase the stress on the growth plate and is therefore a significant cause and a major contributing factor to heel pain in children.
Symptoms
Pain symptoms usually begin after a child begins a new sport or sporting season, and can worsen with athletic activities that involve running and jumping. It is common for a child with Sever?s disease to walk with a limp. Increased activity can lead to heel cord tightness (Achilles Tendon), resulting in pressure on the apophysis of the calcaneus. This will cause irritation of the growth plate and sometimes swelling in the heel area thus producing pain. This usually occurs in the early stages of puberty.
Diagnosis
Sever?s disease is diagnosed based on a doctor?s physical examination of the lower leg, ankle, and foot. If the diagnosis is in question, the doctor may order x-rays or an MRI to determine if there are other injuries that may be causing the heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Activity Modification: to decrease the pain, limiting sporting activities is essential. Cutting back on the duration, intensity, and frequency can significantly improve symptoms. Heel cord stretching is important if heel cord tightness is present. Heel cushions/cups or soft orthotics decreases the impact on the calcaneus by distributing and cushioning the weight bearing of the heel. Use of NSAIDS. Ibuprofen (Nuprin, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) can decrease pain and secondary swelling. Ice. Placing cold or ice packs onto the painful heel can alleviate pain. Short-leg cast. For recalcitrant symptoms a short-leg cast is occasionally used to force rest the heel.
Exercise
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with Severs disease. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 1 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate, advanced and other exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head as far as you can go without pain and provided you feel no more than a mild to moderate stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free. Once you can perform 20 repetitions consistently without pain, the exercise can be progressed by gradually increasing the resistance of the band provided there is no increase in symptoms. Bridging. Begin this exercise lying on your back in the position demonstrated. Slowly lift your bottom pushing through your feet, until your knees, hips and shoulders are in a straight line. Tighten your bottom muscles (gluteals) as you do this. Hold for 2 seconds then slowly lower your bottom back down. Repeat 10 times provided the exercise is pain free.
What Are The Causes Of A Ruptured Achilles Tendon?
Overview
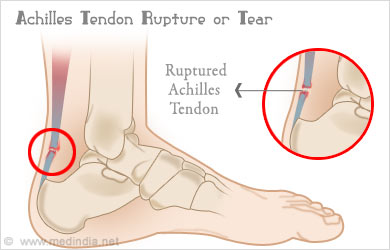 An Achilles tendon rupture is also known as a rupture of the gastrocnemius tendon, or the common calcanean tendon. The tendon is actually composed of 5 different tendons, the two most important being the superficial digital flexor and gastrocnemius tendons. The gastrocnemius tendon is the largest of these, and is the most powerful extensor of the hock (ankle) joint. Both the superficial digital flexor and gastrocnemius tendons attach to the heel bone, called the calcaneus bone. A rupture of the Achilles tendon may be a partial tear, which means just the gastrocnemius is torn, or a complete tear, in which all five tendons have been torn. (show diagrams, normal anatomy vs partial vs complete tears).
An Achilles tendon rupture is also known as a rupture of the gastrocnemius tendon, or the common calcanean tendon. The tendon is actually composed of 5 different tendons, the two most important being the superficial digital flexor and gastrocnemius tendons. The gastrocnemius tendon is the largest of these, and is the most powerful extensor of the hock (ankle) joint. Both the superficial digital flexor and gastrocnemius tendons attach to the heel bone, called the calcaneus bone. A rupture of the Achilles tendon may be a partial tear, which means just the gastrocnemius is torn, or a complete tear, in which all five tendons have been torn. (show diagrams, normal anatomy vs partial vs complete tears).
Causes
Causes of and contributors to Achilles tendon rupture include trauma (caused by injury, usually an acceleration injury such as pushing off or jumping up). Preceding tendon problems. Chronic Achilles tendonitis (can lead to small tears within the tendon, increasingly weakening it). Certain drug therapies/treatments. Drugs that have been linked to Achilles tendon rupture include. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics - after nearly 900 reports of tendon ruptures, tendonitis and other tendon disorders (most associated with the Achilles tendon) linked to Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) alone were collected in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)?s database, at least one public-interest group petitioned the FDA to recommend that a "Black Box Warning" be added to Cipro's packaging. Some researchers speculate this class of antibiotics is toxic to tendon fibers, and that in some cases may reduce their blood supply. Patients should at least be more aware of the potential for ruptures so that they can be switched to other antibiotics at the onset of early warning signals such as tendon pain.
Symptoms
Patients present with acute posterior ankle/heel pain and may give a history of ?felt like someone kicked me from behind?. Patients may report a direct injury, or report the pain started with jumping or landing on a dorsiflexed foot. It is important to elicit in the history any recent steroid or flouroqunolone usage including local steroid injections, and also any history of endocrine disorders or systemic inflammatory conditions.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture is made entirely on physical examination. Often, there is a substantial defect in the Achilles from 2-5 cm before it inserts into the heel bone. However, the main test is to determine whether the Achilles has been ruptured is the Thompson test. This essentially involves placing the patient on their stomach and squeezing the calf muscle. If the Achilles is intact, the foot will rise [plantar flex]. If it is ruptured, the foot will not move and will tend to be in a lower lying position.
Non Surgical Treatment
Two treatment options are casting or surgery. If an Achilles tendon rupture is untreated then it may not heal properly and could lead to loss of strength. Decisions about treatment options should be made on an individual basis. Non-surgical management traditionally is selected for minor ruptures, less active patients, and those with medical conditions that prevent them from undergoing surgery. The goal of casting is to allow the tendon to slowly heal over time. The foot and ankle are positioned to bring the torn ends of the tendon close together. Casting or bracing for up to 12 weeks or more may be necessary. This method can be effective and avoids some risks, such as infection, associated with surgery. However, the likelihood of re-rupture may be higher with a non-surgical approach and recovery can take longer. 
Surgical Treatment
Operative treatment involves a 6cm incision along the inner side of the tendon. The torn ends are then strongly stitched together with the correct tension. After the operation a below knee half cast is applied for 2 weeks. At 2 weeks a brace will be applied that will allow you to move the foot and fully weight-bear for a further 6 weeks. After this you will need physiotherapy. Surgery carries the general risks of any operation but the risk of re-rupture is greatly reduced to 2%. The best form of treatment is controversial with good results being obtained by both methods but surgery is generally recommended for patients under 60 years of age who are fit and active with an intra-substance tear.
Which Are The Key Causes Of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) ?
Overview
PTTD is a common condition treated by foot and ankle specialists. Although there is a role for surgical treatment of PTTD, conservative care often can prevent or delay surgical intervention. Decreasing inflammation and stabilizing the affected joints associated with the posterior tibial tendon can decrease pain and increase functional levels. With many different modalities available, aggressive nonoperative methods should be considered in the treatment of PTTD, including early immobilization, the use of long-term bracing, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. If these methods fail, proper evaluation and work-up for surgical intervention should be employed. 
Causes
A person with flat feet has greater load placed on the posterior tibial tendon which is the main tendon unit supporting up the arch of the foot. Throughout life, aging leads to decreased strength of muscles, tendons and ligaments. The blood supply diminishes to tendons with aging as arteries narrow. Heavier, obese patients have more weight on the arch and have greater narrowing of arteries due to atherosclerosis. In some people, the posterior tibial tendon finally gives out or tears. This is not a sudden event in most cases. Rather, it is a slow, gradual stretching followed by inflammation and degeneration of the tendon. Once the posterior tibial tendon stretches, the ligaments of the arch stretch and tear. The bones of the arch then move out of position with body weight pressing down from above. The foot rotates inward at the ankle in a movement called pronation. The arch appears collapsed, and the heel bone is tilted to the inside. The deformity can progress until the foot literally dislocates outward from under the ankle joint.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch, and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change. For example, when PTTD initially develops, there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon). In addition, the area may be red, warm, and swollen. Later, as the arch begins to flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle. But at this point, the foot and toes begin to turn outward and the ankle rolls inward. As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. The tendon has deteriorated considerably and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic testing is often used to diagnose the condition and help determine the stage of the disease. The most common test done in the office setting are weightbearing X-rays of the foot and ankle. These assess joint alignment and osteoarthritis. If tendon tearing or rupture is suspected, the gold standard test would be MRI. The MRI is used to check the tendon, surrounding ligament structures and the midfoot and hindfoot joints. An MRI is essential if surgery is being considered.
Non surgical Treatment
Flatfoot deformity can be treated conservatively or with surgical intervention depending on the severity of the condition. When people notice their arches flattening, they should immediately avoid non-supportive shoes such as flip-flops, sandals or thin-soled tennis shoes. Theses shoes will only worsen the flatfoot deformity and exacerbate arch pain. Next, custom orthotics are essential for people with collapsed arches. Over-the-counter insoles only provide cushion and padding to the arch, whereas custom orthotics are fabricated to specifically fit the patient?s foot and provide support in the arch where the posterior tibial tendon is unable to anymore. Use of custom orthotics in the early phases of flatfoot or PTTD can prevent worsening of symptoms and prevent further attenuation or injury to the posterior tibial tendon. In more severe cases of flatfoot deformity an ankle foot orthosis (AFO) such as a Ritchie brace is needed. This brace provides more support to the arch and hindfoot rather than an orthotic but can be bulky in normal shoegear. Additional treatment along with use of custom orthotics is use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDS) such as Advil, Motrin, or Ibuprofen which can decrease inflammation to the posterior tibial tendon. If pain is severe, the patient may need to be placed in a below the knee air walker boot for several weeks which will allow the tendon to rest and heal, especially if a posterior tibial tendon tear is noted on MRI. 
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatment fails surgical intervention is offered. For a Stage 1 deformity a posterior tibial tendon tenosynovectomy (debridement of the tendon) or primary repair may be indicated. For Stage 2 a combination of Achilles lengthening with bone cuts, calcaneal osteotomies, and tendon transfers is common. Stage 2 flexible PTTD is the most common stage patients present with for treatment. In Stage 3 or 4 PTTD isolated fusions, locking two or more joints together, maybe indicated. All treatment is dependent on the stage and severity at presentation with the goals and activity levels of the patient in mind. Treatment is customized to the individual patient needs.